Electricity 101: Understanding the Basics
Key Electrical Terms Every Property Owner Should Know
Electricity powers nearly everything in modern life. From lighting and appliances to complex industrial systems, it keeps homes and businesses running efficiently. Yet for many people, the principles behind electricity remain a mystery. Understanding a few basic electrical terms can make it easier to grasp how power systems work and why professional expertise is so important for safety and performance.
At ESD Electric, we believe that informed customers make better decisions about their electrical systems. This introduction covers key terms such as voltage, current, and resistance, along with basic safety concepts that every property owner should know.
What Is Electricity?
Electricity is the movement of electrons through a conductor, such as copper wire. These moving electrons create an electric current that can be used to power lights, machinery, and electronic devices. The rate, pressure, and resistance of this flow determine how energy is delivered and how efficiently it operates.
In its simplest form, an electrical system consists of a source (like a battery or power plant), a pathway (the wiring), and a load (anything that consumes electricity, such as a lamp or appliance). Understanding how these components interact is essential to both functionality and safety.

Key Electrical Terms Explained
Voltage (Volts)
Voltage is the electrical “pressure” that pushes current through a circuit. It is measured in volts (V). Think of voltage as the force that drives electricity from one point to another. Residential systems in the United States typically use 120 or 240 volts, depending on the appliance.
Current (Amperes)
Current, measured in amperes or “amps” (A), represents the flow of electrical charge. Higher current means more electrons are moving through the wire at a given time. Household circuits are usually rated between 15 and 20 amps, while heavy-duty equipment may require higher ratings.

Resistance (Ohms)
Resistance, measured in ohms (Ω), describes how much a material opposes the flow of electricity. Conductors like copper have very low resistance, allowing current to move easily, while insulators like rubber have high resistance, preventing the flow. The right balance of resistance ensures that equipment functions efficiently and safely.
Power (Watts)
Power, measured in watts (W), indicates how much energy is being consumed by a device. It is calculated using the formula Power = Voltage × Current. For example, a 100-watt light bulb operating at 120 volts uses about 0.83 amps of current.
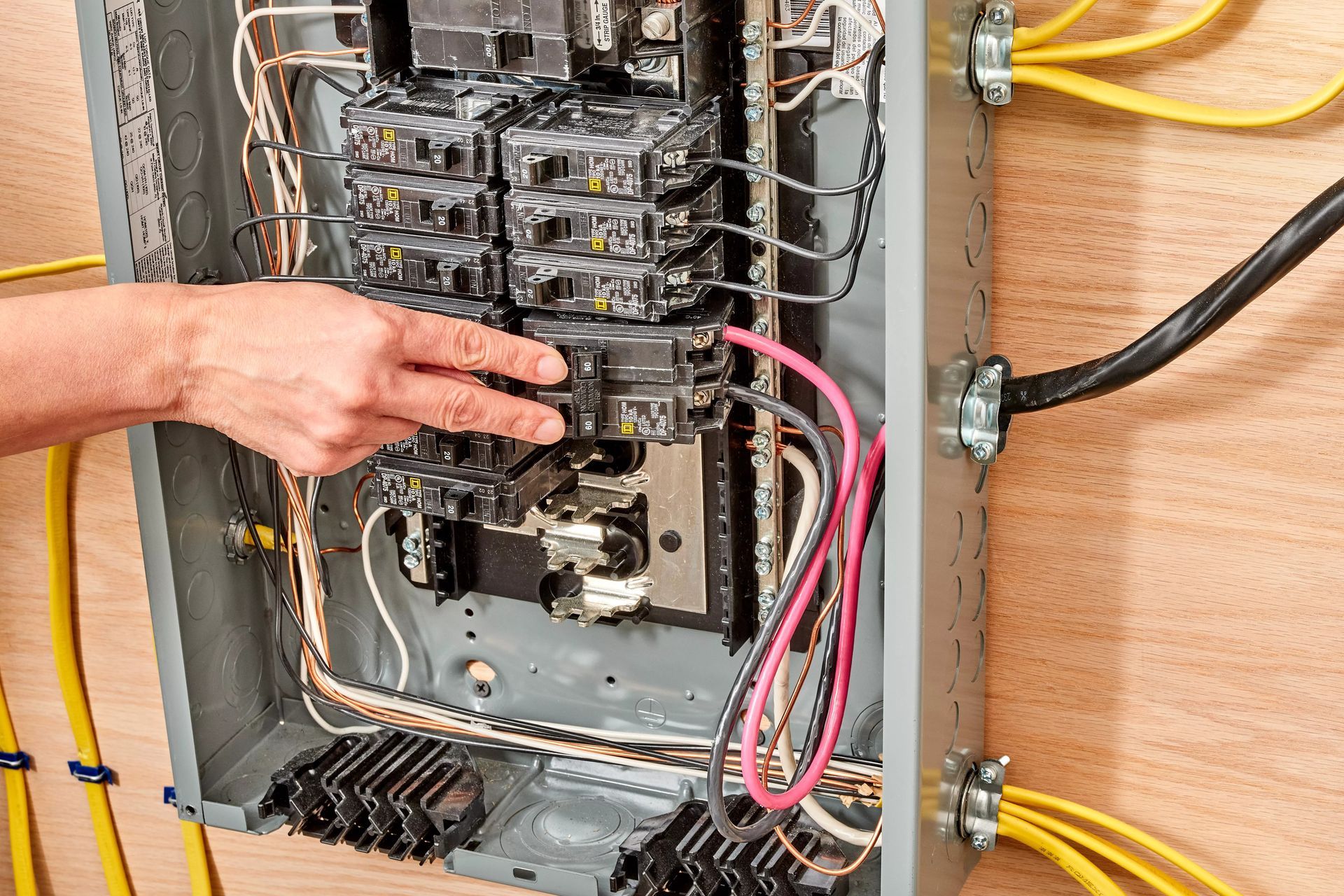
Understanding these measurements helps explain why circuit breakers exist. They are designed to interrupt power when current exceeds safe limits, preventing overheating and potential electrical fires.

Basic Electrical Safety
Electricity is powerful, and when handled improperly, it can be dangerous. Even small residential circuits carry enough current to cause injury. That is why electrical work should always be performed by licensed professionals who understand safety standards and local building codes.
Here are a few basic safety principles to keep in mind:
- Never overload circuits. Plugging too many devices into a single outlet can cause wires to overheat and breakers to trip.
- Inspect cords and outlets regularly. Damaged insulation or loose connections can expose live wires and increase fire risk.
- Keep water and electricity separate. Moisture conducts electricity, which makes bathrooms, kitchens, and outdoor areas particularly hazardous if not properly grounded.
Know where your circuit breakers are. In an emergency, shutting off power quickly can prevent damage and save lives.

Why Professional Electrical Service Matters
While learning the basics of electricity helps you understand how systems operate, professional expertise ensures that they function safely and efficiently. Electricians are trained to design, install, and maintain systems that meet OSHA and National Electrical Code (NEC) standards.
At ESD Electric, our technicians use advanced tools to test voltage, continuity, and resistance, ensuring every component operates as intended. Whether upgrading service panels, rewiring older systems, or troubleshooting power issues, professional electrical care minimizes risks and extends the life of your investment.

Powering Knowledge and Safety
Electricity may seem complex, but its principles are consistent and predictable when understood correctly. Knowing what voltage, current, resistance, and power mean can help property owners make informed decisions about their electrical needs.
When questions arise or new projects require expert attention, professional service is the safest and most efficient solution. At ESD Electric, we provide dependable, code-compliant electrical work across Southern California, helping homes and businesses stay powered, efficient, and safe.
Contact ESD Electric today to schedule a consultation and discover how professional electrical expertise can keep your property running smoothly and safely.